Make with Ada 2020: The autonomous firetruck
The AFT (Autonomous FireTruck) is a prototype of an autonomous firetruck that can put out fire without risking people's lives. This project won a finalist prize in the Make with Ada 2019/20 competition.
The AFT (Autonomous FireTruck) is a prototype of an autonomous firetruck that can put out fire without risking people's lives. This project won a finalist prize in the Make with Ada 2019/20 competition.
Guillermo Perez's project won a finalist prize in the Make with Ada 2019/20 competition. This project was originally posted on Hackster.io here. For those interested in participating in the 2020/21 competition, registration is now open and project submissions will be accepted until Jan 31st 2021, register here.
Welcome to the Ada for micro:bit series where we look at simple examples to learn how to program the BBC micro:bit with Ada.
A few years ago we realized that having a package manager for the Ada/SPARK community would be a game changer. Since then, AdaCore has been sponsoring and contributing to the Alire project created by Alejandro Mosteo from the Centro Universitario de la Defensa de Zaragoza. With this blog post I want to introduce Alire and explain why this project is important for the `Ada`/`SPARK` community.
Blaine Osepchuk's project won a finalist prize in the Make with Ada 2019/20 competition. This project was originally posted on Hackster.io here. For those interested in participating in the 2020/21 competition, registration is now open and project submissions will be accepted until Jan 31st 2021, register here.
Laurent Zhu's and Damien Grisonnet's project was accomplished for the EPITA Ada courses and won a finalist prize in the Make with Ada 2019/20 competition.
Welcome to the Ada for micro:bit series where we look at simple examples to learn how to program the BBC micro:bit with Ada.
Welcome to the Ada for micro:bit series where we look at simple examples to learn how to program the BBC micro:bit with Ada.
This is the second post of a series about GNATcoverage and source code instrumentation. The previous post introduced how GNATcoverage worked originally and why we extended it to support source instrumentation-based code coverage computation. Let’s now see it in action in the most simple case: a basic program running on the host machine, i.e. the Linux/Windows machine that runs GNATcoverage itself.
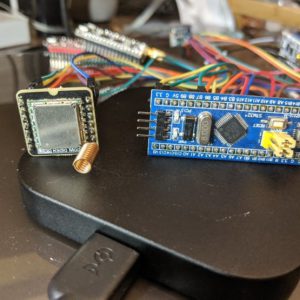
Hedley Rainnie's project combines 6 different SoCs all programmed in Ada performing as a LoRa network. He also showcases a BLE bridge to a LoRa server. His project came about when him and his wife were musing about how to detect and deter unwanted garden visitors. This ongoing project won a finalist prize in the 2019/20 Make with Ada competition.
Shahariar's project ensures safety against electrical fire or shock during an earthquake, flood, gas leakage or fire breakout by disconnecting the mains with a smart circuit breaker. Additionally, this project won a finalist prize in the 2019/20 Make with Ada competition.
Team CryptAda's project collects entropy, manages an entropy pool, implements a homemade PRNG, and generates RSA keys directly on the board with an accent on security. Additionally, this project won a finalist prize in the 2019/20 Make with Ada competition.
John Singleton's The SmartBase makes your existing adjustable bed safer and easier to use by adding voice control and safe (and fun!) LED underbed lighting! Additionally, this project won first place prize in the 2019/20 Make with Ada competition.
Last year, I started evaluating programming languages for a formally-verified operating system. I've been developing software for a while, but only recently began work in high integrity software development and formal methods. There are several operating system projects, like the SeL4 microkernel and the Muen separation kernel, that make use of formal verification. But I was interested in using a formally-verified language to write a general-purpose OS - an environment for abstracting the underlying hardware while acting as an arbiter for running the normal applications we're used to.
This blog entry describes the transformation of an Ada stack ADT into a completely proven SPARK implementation that relies on static verification instead of run-time enforcement of the abstraction’s semantics. We will prove that there are no reads of unassigned variables, no array indexing errors, no range errors, no numeric overflow errors, no attempts to push onto a full stack, no attempts to pop from an empty stack, that subprogram bodies implement their functional requirements, and so on. As a result, we get a maximally robust implementation of a reusable stack abstraction providing all the facilities required for production use.
Over the last few months, I developed a SPARK version of the TweetNaCl cryptographic library. This was made public on GitHub in February 2020, under the 2-clause BSD licence. This blog entry goes into a bit more technical detail on one particular aspect of the project: the challenge of re-writing and verifying "constant time" algorithms using SPARK.
Learn how to use GDB and RR's advanced time traveling features in GNAT Studio.
Having previously shown how to create a Web application in Ada, it's not so difficult to create an Android application in Ada. Perhaps the simplest way is to install Android Studio. Then just create a new project and choose "Empty Activity". Open the layout, delete TextView and put WebView instead.
As a demonstration for the use of Ada and SPARK in very small embedded targets, I created a remote-controlled (RC) car using Lego NXT Mindstorms motors and sensors but without using the Lego computer or Lego software. I used an ARM Cortex System-on-Chip board for the computer, and all the code -- the control program, the device drivers, everything -- is written in Ada. Over time, I’ve upgraded some of the code to be in SPARK. This blog post describes the hardware, the software, the SPARK upgrades, and the repositories that are used and created for this purpose.
Martyn’s recent blog post showed small programs based on Libadalang to find uses of access types in Ada sources. Albeit short, these programs need to take care of all the tedious logistics around processing Ada sources: find the files to work on, create a Libadalang analysis context, use it to read the source files, etc. Besides, they are not very convenient to run: