Formal Verification of Legacy Code
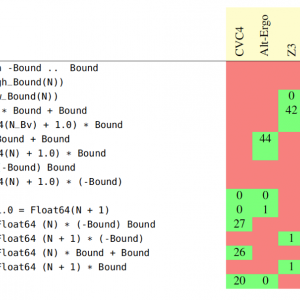
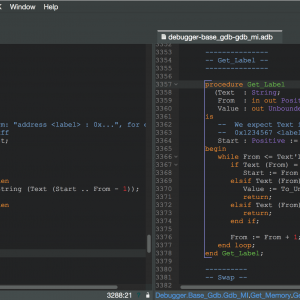
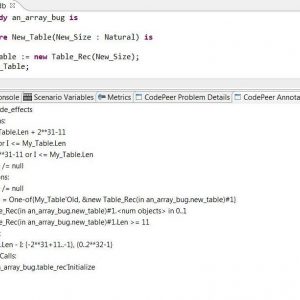
Just a few weeks ago, one of our partners reported a strange behavior of the well-known function Ada.Text_IO.Get_Line, which reads a line of text from an input file. When the last line of the file was of a specific length like 499 or 500 or 1000, and not terminated with a newline character, then Get_Line raised an exception End_Error instead of returning the expected string. That was puzzling for a central piece of code known to have worked for the past 10 years! But fair enough, there was indeed a bug in the interaction between subprograms in this code, in boundary cases having to do with the size of an intermediate buffer. My colleague Ed Schonberg who fixed the code of Get_Line had nonetheless the intuition that this particular event, finding such a bug in an otherwise trusted legacy piece of code, deserved a more in depth investigation to ensure no other bugs were hiding. So he challenged the SPARK team at AdaCore in checking the correctness of the patched version. He did well, as in the process we uncovered 3 more bugs.