The Make with Ada competition is back!
AdaCore’s fourth annual Make with Ada competition launched this week with over $8K in cash and prizes to be awarded for the most innovative embedded systems projects developed using Ada and/or SPARK.
AdaCore’s fourth annual Make with Ada competition launched this week with over $8K in cash and prizes to be awarded for the most innovative embedded systems projects developed using Ada and/or SPARK.
The Ada Community has gathered recently around a new exciting initiative - an Ada Virtual Conference, to present Ada-related topics in a 100% remote event. The first such conference took place on August, 10th 2019, around the topic of the new features in Ada 202x. Here is what was presented.
The challenge faced by cryptography APIs is to make building functional and secure programs easy for the user. In this blog post I will present you how I created a SPARK binding for Libsodium, using strong typing and preconditions/postconditions to enforce a safe and functional use of basic cryptographic primitives.
The functionality of many security-critical programs is directly related to Input/Output (I/O). This includes command-line utilities such as gzip, which might process untrusted data downloaded from the internet, but also any servers that are directly connected to the internet, such as webservers, DNS servers and so on. In this blog post we show an approach that deals with error handling and reasoning about content, and demonstrate the approach using the cat command line utility.
I am an Associate Professor at Polytechnic University of Madrid’s (Universidad Politécnica de Madrid / UPM) in the Department of Architecture and Technology of Computer Systems. For the past several years I have been directing a team of colleagues and students in the development of a UPMSat-2 microsatellite. The project originally started in 2013 as a follow-to the UPM-SAT 1, launched by an Ariane-4 in 1995.
Interested in participating in the evolution of the Ada or SPARK languages? We have something for you.
In this blog post, I will present one of the most interesting additions to the community 2019 version of SPARK: pointer support. One of the core assumption in SPARK has always been the absence of aliasing, so adding pointers without breaking this assumption was quite a challenge. I will explain how this was achieved using an ownership model for pointers (like is done in Rust) through small examples.
We are pleased to announce that GNAT Community 2019 has been released! See https://www.adacore.com/download.
C is the dominant language of the embedded world, almost to the point of exclusivity. Due to its age, and its goal of being a “portable assembler”, it deliberately lacks type-safety, opening up exploit vectors. Proposed solutions are partitioning the application into smaller intercommunicating blocks, designed with the principle of least privilege in mind; and rewriting the application in a type-safe language. We believe that both approaches are complementary and want to show you how to combine separation and isolation provided by MultiZone together with iteratively rewriting parts in Ada. We will take the MultiZone SDK demo and rewrite one of the zones in Ada.
The Danish Technical University has a yearly RoboCup where autonomous vehicles solve a number of challenges. We participated with RoadRunner, a 3D printed robot with wheel suspension, based on the BeagleBone Blue ARM-based board and the Pixy 1 camera with custom firmware enabling real-time line detection. Code is written in Ada and formally proved correct with SPARK at Silver level.
In 2014, Adam Langley, a well-known cryptographer from Google, wrote a post on his personal blog, in which he tried to prove functions from curve25519-donna, one of his projects, using various verification tools: SPARK, Frama-C, Isabelle... He describes this attempt as "disappointing", because he could not manage to prove "simple" things, like absence of runtime errors. I will show in this blogpost that today, it is possible to prove what he wanted to prove, and even more.
This course is geared to software professionals looking for a practical introduction to the Ada language with a focus on embedded systems, including real-time features as well as critical features introduced in Ada 2012. By attending this course you will understand and know how to use Ada for both sequential and concurrent applications, through a combination of live lectures from AdaCore's expert instructors and hands-on workshops using AdaCore's latest GNAT technology. AdaCore will provide an Ada 2012 tool-chain and ARM-based target boards for embedded workshops. No previous experience with Ada is required.
A question that our users sometimes ask us is "do you use CodePeer at AdaCore and if so, how?". The answer is yes! and this blog post will hopefully give you some insights into how we are doing it for our own needs.
My colleague, Carl Brandon, and I have been running the CubeSat Laboratory at Vermont Technical College (VTC) for over ten years. During that time we have worked with nearly two dozen students on building and programming CubeSat nano satellites. Because of their general inexperience, and because of the high student turnover rate that is natural in an educational setting, our development process is often far from ideal. Here SPARK has been extremely valuable to us. What we lack in rigor of the development process we make up for in the rigor of the SPARK language and tools. In November 2013 we launched a low Earth orbiting CubeSat. The launch vehicle contained 13 other university built CubeSats. Most were never heard from. One worked for a few months. Ours worked for two years until it reentered Earth's atmosphere as planned in November 2015.
MISRA C is the most widely known coding standard restricting the use of the C programming language for critical software. For good reasons. For one, its focus is entirely on avoiding error-prone programming features of the C programming language rather than on enforcing a particular programming style. In addition, a large majority of rules it defines are checkable automatically (116 rules out of the total 159 guidelines), and many tools are available to enforce those. As a coding standard, MISRA C even goes out of its way to define a consistent sub-language of C, with its own typing rules (called the "essential type model" in MISRA C) to make up for the lack of strong typing in C.
Like last year, we've sent a squad of AdaCore engineers to participate in the celebration of Open Source software at FOSDEM. Like last year, we had great interactions with the rest of the Ada and SPARK Community in the Ada devroom on Saturday. That's what we have to say about it.
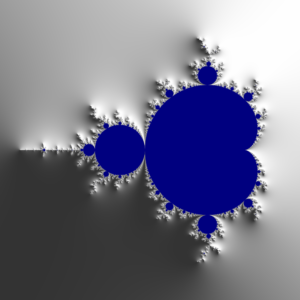
In Part 1 of this blog post I discussed why I chose to implement this application using the Ada Web Server to serve the computed fractal to a web browser. In this part I will discuss a bit more about the backend of the application, the Ada part.
The is the first part of a multiple part post that covers the development of the AdaFractal project. The idea was to create fractals in Ada. Here we will cover how to use AWS to create a flexible and portable way to display the generated fractals without using bulky graphics libraries.
Over the past several years, a great number of public announcements have been made about companies that are either studying or adopting the Ada and SPARK programming languages. Noteworthy examples include Dolby, Denso, LASP and Real Heart, as well as the French Security Agency.
The promise behind the SPARK language is the ability to formally demonstrate properties in your code regardless of the input values that are supplied - as long as those values satisfy specified constraints. As such, this is quite different from static analysis tools such as our CodePeer or the typical offering available for e.g. the C language, which trade completeness for efficiency in the name of pragmatism. Indeed, the problem they’re trying to solve - finding bugs in existing applications - makes it impossible to be complete. Or, if completeness is achieved, then it is at the cost of massive amount of uncertainties (“false alarms”). SPARK takes a different approach. It requires the programmer to stay within the boundaries of a (relatively large) Ada language subset and to annotate the source code with additional information - at the benefit of being able to be complete (or sound) in the verification of certain properties, and without inundating the programmer with false alarms.