New SPARK Cheat Sheet
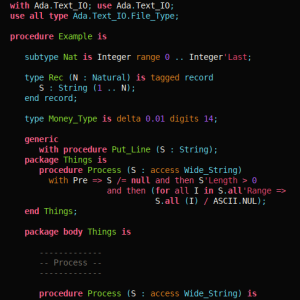
Our good friend Martin Becker has produced a new cheat sheet for SPARK, that you may find useful for a quick reminder on syntax that you have not used for some time.
Our good friend Martin Becker has produced a new cheat sheet for SPARK, that you may find useful for a quick reminder on syntax that you have not used for some time.
While we are working very hard on semantic analysis in Libadalang, it is already possible to leverage its lexical and syntactic analyzers. A useful example for this is a syntax highlighter.
When things don’t work as expected, developers usually do one of two things: either add debug prints to their programs, or run their programs under a debugger. Today we’ll focus on the latter activity.
For all the power that comes with proof technology, one sometimes has to pay the price of writing a loop invariant. Along the years, we've strived to facilitate writing loop invariants by improving the documentation and the technology in different ways, but writing loops invariants remains difficult sometimes, in particular for beginners. To completely remove the need for loop invariants in simple cases, we have implemented loop unrolling in GNATprove. It turns out it is quite powerful when applicable.
A friend pointed me to recent posts by Tommy M. McGuire, in which he describes how Frama-C can be used to functionally prove a brute force version of string search, and to find a previously unknown bug in a faster version of string search called quick search. Frama-C and SPARK share similar history, techniques and goals. So it was tempting to redo the same proofs on equivalent code in SPARK, and completing them with a functional proof of the fixed version of quick search. This is what I'll present in this post.
For those users of the GNAT GPL edition, we are pleased to announce the availability of the 2017 release of GNAT GPL and SPARK GPL.
Updated July 2018
A few weeks ago one of my colleagues shared this kickstarter project : The Barisieur. It’s an alarm clock coffee maker, promising to wake you up with a freshly brewed cup of coffee every morning. I jokingly said “just give me an espresso machine and I can do the same”. Soon after, the coffee machine is in my office. Now it is time to deliver :)
We reported in a previous post our initial experiments to create lightweight checkers for Ada source code, based on the new Libadalang technology. The two checkers we described discovered 12 issues in the codebase of the tools we develop at AdaCore. In this post, we are reporting on 6 more lightweight checkers, which have discovered 114 new issues in our codebase. This is definitely showing that these kind of checkers are worth integrating in static analysis tools, and we look forward to integrating these and more in our static analyzer CodePeer for Ada programs.
After we created lightweight checkers based on the recent Libadalang technology developed at AdaCore, a colleague gave us the challenge of creating a copy-paste detector based on Libadalang. It turned out to be both easier than anticipated, and much more efficient and effective than we could have hoped for. In the end, we hope to use this new detector to refactor the codebase of some of our tools, and we expect to integrate it in our IDEs.
In my previous blog article, I exposed some techniques that helped me rewrite the Crazyflie’s firmware from C into Ada and SPARK 2014, in order to improve its safety.
User friendly strings APIIn a previous post, we described the design of a new strings package, with improved performance compared to the standard Ada unbounded strings implementation. That post focused on various programming techniques used to make that package as fast as possible.
Euclid's algorithm for computing the greatest common divisor of two numbers is one of the first ones we learn in school, and also one of the first algorithms that humans devised. So it's quite appealing to try to prove it with an automatic proving toolset like SPARK. It turns out that proving it automatically is not so easy, just like understanding why it works is not so easy. In this post, I am using ghost code to prove correct implementations of the GCD, starting from a naive linear search algorithm and ending with Euclid's algorithm.
This post describes the new GNATCOLL.Strings package, and the various optimizations it performs to provide improved performance.
This post has been updated in March 2017 and was originally posted in March 2016.
Following the current trend, the GNATcoverage project moves to GitHub! Our new address is: https://github.com/AdaCore/gnatcoverage
GNATprove performs auto-active verification, that is, verification is done automatically, but usually requires annotations by the user to succeed. In SPARK, annotations are most often given in the form of contracts (pre and postconditions). But some language features, in particular ghost code, allow proof guidance to be much more involved. In a paper we are presenting at NASA Formal Methods symposium 2017, we describe how an imperative red black tree implementation in SPARK was verified using intensive auto-active verification.
The Ada Drivers Library (ADL) is a collection of Ada device drivers and examples for ARM-based embedded targets. The library is maintained by AdaCore, with development originally (and predominantly) by AdaCore personnel but also by the Ada community at large. It is available on GitHub and is licensed for both proprietary and non-proprietary use.
At AdaCore, we have a strong expertise in deep static analysis tools (CodePeer and SPARK), and we have been relying on the compiler GNAT and our coding standard checker GNATcheck to deal with more syntactic or weakly-semantic checks. The recent Libadalang technology, developed at AdaCore, provided us with an ideal basis to develop specialized light-weight static analyzers. As an experiment, we implemented two simple checkers using the Python binding of Libadalang. The results on our own codebase were eye-opening: we found a dozen bugs in the codebases of the tools we develop at AdaCore (including the compiler and static analyzers).
AdaCore is working on a host of tools that works on Ada code. The compiler, GNAT, is the most famous and prominent one, but it is far from being the only one. At AdaCore, we already have several other tools to process Ada code: the ASIS library, GNAT2XML, the GPS IDE. A realization of the past years, however, has been that we were lacking a unified solution to process code that is potentially evolving, potentially incorrect Ada code. Hence Libadalang.