GNAT Static Analysis Suite Gitlab Integration - Scaling the pipeline up
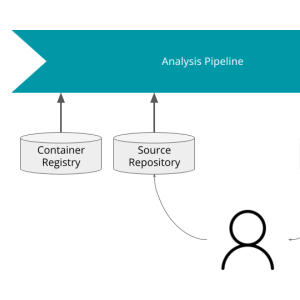
In the previous blog post of this series, we set up a GNAT Static Analysis Suite (GNAT SAS) analysis pipeline. This post focuses on the pipeline's maintainability, security, and user experience.In this post, we will describe solutions to these issues by detailing the pipeline design and how to automate its update, and integrating a script to ease conducting and pushing reviews. Finally we’ll review using GitLab native analysis tooling to improve the user experience and gain a branch-aware analysis overview.