
I can’t believe that I can prove that it can sort
When an enthusiastic Ada programmer and a SPARK expert pair up to prove the most "stupid" sorting algorithm, lessons are learned! Join us in this eye-opening journey.
2 entries tagged with #Proof

When an enthusiastic Ada programmer and a SPARK expert pair up to prove the most "stupid" sorting algorithm, lessons are learned! Join us in this eye-opening journey.
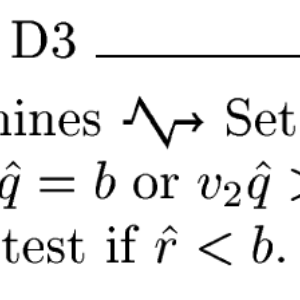
The GNAT light runtime library is a version of the runtime library targeted at embedded platforms and certification, which has been certified for use at the highest levels of criticality in several industrial domains. It contains around 180 units focused mostly on I/O, numerics, text manipulation, memory operations. We have used SPARK to prove the correctness of 40 of them: that the code is free of runtime errors, and that it satisfies its functional specifications.